Lupine Publishers|Environmental journals
Water pollution gained worldwide attention due to the severity of the
concern where many places of the world are going through
the drought and groundwater pollution. Pharmaceuticals and personal care
products (PPCPs). PPCPs are the unadorned and
noxious pollutants, although water purification processes by various
techniques as bioremediation, phytoremediation, conventional
wastewater treatment etc. are taking place. For PPCPs, there are no
specific method is discovered yet where convention treatment
is found inappropriate for the same. This research will lead the PPCPs
removal from the industrial wastewater, which comprises the
photo catalysis as well as absorbent method. Photo catalysis, an
emerging concept is trusted as effective treatment methods for the
removal and determination of PPCPs from wastewater treatment because of
the efficiency and feasibility. Furthermore, a detailed
studyis required on blending other techniques with the photo catalysis
like Advance Oxidation Process (AOP)and absorbent method.
This research will focus on the thorough purification of PPCPs from
wastewater through Photo-catalysis and Advance Oxidation
Process (AOP) [1,2].
Keywords: Wastewater; PPCPs; Photo catalysis; Wastewater Treatment
Water is the basic component that supports life on the earth
and the precious natural resource. Water pollution is the key
concern worldwide, which is to be a cure at every level. Industrial
wastewater is treated at every possible way and it is utilized
for the irrigation and aquaculture. India is holding the third
position in terms of Pharmaceutical industries by volume. Which
contribute a large variant of water pollutant in low concentration.
Pharmaceutical and Personal care Products (PPCPs) are the
emerging pollutants in wastewater, which is not efficient removed
even after the conventional wastewater treatment. However, it may
not cause any immediate effect to the life on the earth, but it may
be big concern when it will be exposed a longer period [3-5]. The
scientific and industrial communities are still a long way from the
most effective, economic and applicable methods to reach these
goals and overcome the current WWTP challenges. Although the
challenges of the removal of PPCPs from wastewater treatment are
significant, a number of these challenges are possibly temporary,
including economic, technical and environmental hurdles. A serious
collaboration between research, industrial and governmental
sectors is essential to solving these challenges. There are some
researches, which is taking place in various research centers
worldwide [6].
Currently, in the available literature, most studies Advance Oxidation Processes are Fenton Oxidation process, Ozone Oxidation, H2O2 Oxidation, Electrochemical methods and Nonchemical methods as well as photochemical degradation using UV. It is found, there is a need to coupled advance oxidation processes. PPCPs can be removed efficiently by using Physical and biological agents combined. Therefore, the biological couplings with chemical techniques are not covered yet in the literature. It may produce the efficient removal of PPCPs from the wastewater [7].
L. T. Lemmuel et al. (2018) elaborated about the recent
research on PPCPs removal. Study states that the advances in
analytical chemistry instrumentation, low levels of PPCPs can
now be detected by mass spectroscopy which may be coupled
to either liquid or gas chromatography. Adsorption is the most
popular physical method, which is often used for removal of trace
organic pollutants in water and one of the main processes for removing PPCPs in the environment. For biological approaches
the use of microbes for degradation processes are the most
important removal mechanism for organic pollutants in the
environment, which has many advantages such as low cost and
mild operational conditions. Microbes in either pure culture or
mixed cultures can remove the pollutants by utilizing the essential
elements or the carbon backbone of the PPCPs for their metabolic
functions and in most cases the microbial consortia cooperate
together in the removal of the pollutants. Some of the well-known
advanced oxidation (AO) methods are ozonation, UV oxidation
processes, conventional Fenton oxidation and Fenton-like systems,
photocatalysis, ultrasonication (US) and electrochemical methods,
while rapidly evolving advanced oxidation technologies include
ionizing radiation, microwaves, pulsed plasma and the use of ferrate
reagent. Current technologies for AOPs can be employed either
alone or in combination with other physico-chemical or biological
processes for actual wastewater treatment [8].
J. E.Anekwe et al. (2017) explained that PPCPs are a group of emerging contaminants with physicochemical characteristics that distinguish them from other contaminants (e.g. persistent organic pollutants). Pharmaceuticals are structurally designed to maximize their biological activity at low concentrations and developed to produce a prolonged action. These properties highlight the risks associated with the inadvertent presence of PPCPs in the environment. S. Honglan et al (2012) concluded in his study that emerging contaminant compounds occur in trace concentrations in waters, their adverse effects to aquatic organisms, animals, and humans cannot be underestimated due to their continuous release into the water systems. The assessment and removal of emerging contaminants and their transformation products in natural and drinking waters are challenging tasks because of the complexity of contaminants in water samples. However, tremendous progress has been made on assessment of many emerging contaminants due to the great efforts and times committed by many scientists working in different research fields. The effectiveness of the treatment depends not only on the properties of the technique, but also on various environmental conditions and variables used for the processes, e.g. in physical removal process, it depends on pH, ionic strength, temperature, existence of competing organic or inorganic compounds in solution, initial adsorb ate and adsorbent concentration, contact time and speed of rotation, particle size of adsorbent, etc [9].
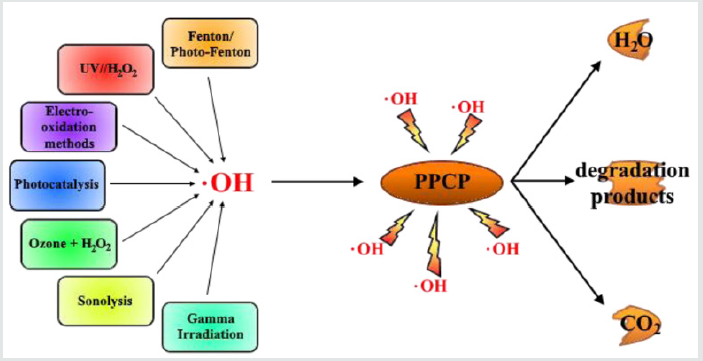
S. Esplugas et al. (2007) studied and stated AOPs (Advanced oxidation processes) such as UV/H2O2 or UV/O3 processes should be considered for their effective removal. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) constitute a promising technology for the treatment of wastewaters containing pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and especially endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs). Data concerning the degradation of PPCPs and EDCs by means of AOPs. Ozonation is the oxidation process most studied, gives the best expectative because feasible techniques need to be in place to remove them or at least reduced them below the regulated levels. Identification of the contaminants PPCPs can be done with the help of HPLC, GC-MS and LC-MS etc. whereas the removal of PPCPs can be experiment by using various absorbents and Photo-catalytic agents (Figure 1) [10].
Analytical and environmental application Such as removal of
PPCPs, reduction of a waterborne pathogen or antibacterial tests as
well as physicochemical analysis of industrial wastewater quality,
it helps to achieve the sustainable development goals for e.g. clean
water and sanitation. More attention and efforts should be given to
these topics to be developed and know all details concerning the
toxicity of PPCPs and how can be removed from our environment.
Abstract
Keywords: Wastewater; PPCPs; Photo catalysis; Wastewater Treatment
Introduction
Currently, in the available literature, most studies Advance Oxidation Processes are Fenton Oxidation process, Ozone Oxidation, H2O2 Oxidation, Electrochemical methods and Nonchemical methods as well as photochemical degradation using UV. It is found, there is a need to coupled advance oxidation processes. PPCPs can be removed efficiently by using Physical and biological agents combined. Therefore, the biological couplings with chemical techniques are not covered yet in the literature. It may produce the efficient removal of PPCPs from the wastewater [7].
Literature Review
J. E.Anekwe et al. (2017) explained that PPCPs are a group of emerging contaminants with physicochemical characteristics that distinguish them from other contaminants (e.g. persistent organic pollutants). Pharmaceuticals are structurally designed to maximize their biological activity at low concentrations and developed to produce a prolonged action. These properties highlight the risks associated with the inadvertent presence of PPCPs in the environment. S. Honglan et al (2012) concluded in his study that emerging contaminant compounds occur in trace concentrations in waters, their adverse effects to aquatic organisms, animals, and humans cannot be underestimated due to their continuous release into the water systems. The assessment and removal of emerging contaminants and their transformation products in natural and drinking waters are challenging tasks because of the complexity of contaminants in water samples. However, tremendous progress has been made on assessment of many emerging contaminants due to the great efforts and times committed by many scientists working in different research fields. The effectiveness of the treatment depends not only on the properties of the technique, but also on various environmental conditions and variables used for the processes, e.g. in physical removal process, it depends on pH, ionic strength, temperature, existence of competing organic or inorganic compounds in solution, initial adsorb ate and adsorbent concentration, contact time and speed of rotation, particle size of adsorbent, etc [9].
S. Esplugas et al. (2007) studied and stated AOPs (Advanced oxidation processes) such as UV/H2O2 or UV/O3 processes should be considered for their effective removal. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) constitute a promising technology for the treatment of wastewaters containing pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and especially endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs). Data concerning the degradation of PPCPs and EDCs by means of AOPs. Ozonation is the oxidation process most studied, gives the best expectative because feasible techniques need to be in place to remove them or at least reduced them below the regulated levels. Identification of the contaminants PPCPs can be done with the help of HPLC, GC-MS and LC-MS etc. whereas the removal of PPCPs can be experiment by using various absorbents and Photo-catalytic agents (Figure 1) [10].
Conclusion
For more Lupine
Publishers Open Access Journals Please visit our website:
http://lupinepublishers.us/
For more Open Access Journal on Environmental and Soil Sciences articles Please Click Here:
https://lupinepublishers.com/environmental-soil-science-journal/
http://lupinepublishers.us/
For more Open Access Journal on Environmental and Soil Sciences articles Please Click Here:
https://lupinepublishers.com/environmental-soil-science-journal/
To Know More About Open Access Publishers Please Click on Lupine Publishers

No comments:
Post a Comment